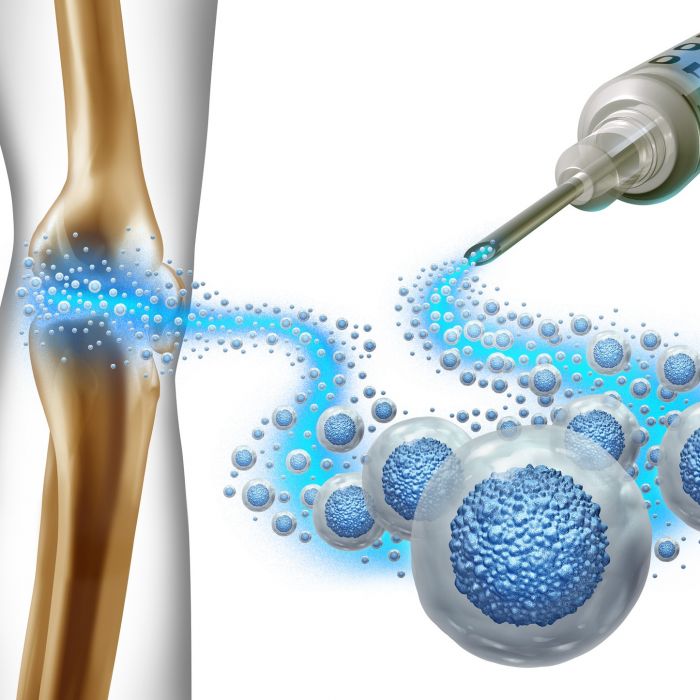
Aging is an inevitable part of life, but with recent scientific advances, the quest for the “fountain of youth” has gained unprecedented momentum. Central to this narrative is the potential of stem cells in anti-aging therapies. As the foundational cells from which all specialized cells in our bodies arise, stem cells offer a reservoir of repair and rejuvenation possibilities. Let’s delve into how these cells might revolutionize anti-aging treatments.
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the capacity to differentiate into any cell type in the body, whether that’s a skin cell, a heart muscle cell, or a nerve cell. They also possess the unique ability to self-renew, meaning they can divide and produce more stem cells. This dual capability – differentiation and self-renewal – renders stem cells especially promising for anti-aging interventions.
Stem cells are naturally occurring cells that are ethically harvested from several sources. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are derived from embryos. These cells are pluripotent, which means they can become almost any type of cell in the body. Adult (or somatic) stem cells are present in various tissues of the adult body. These are more specialized than ESCs. For instance, hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow generate all the types of blood cells. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells reprogrammed to function like embryonic stem cells, providing a potentially limitless source of personalized cells for therapies.
Stem Cells and Aging: What’s the Link?
Aging involves a range of cellular and molecular alterations. Key mechanisms encompass DNA damage, telomere shortening, reduced autophagy, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Simultaneously, our reservoir of stem cells depletes over time, compromising the body’s innate repair mechanisms.
Researchers theorize that boosting the body’s stem cell count or rejuvenating existing stem cells might counteract age-related decline. Here’s how:
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: As our body ages, the capacity to repair and regenerate diminishes. By introducing fresh stem cells, the speed and efficiency of tissue repair could be enhanced.
- Cell Replacement: Degenerative diseases, often linked to aging, result from the loss or dysfunction of specific cell types. Stem cells could potentially replace these lost cells. For instance, in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the loss of retinal cells could be reversed by transplanting retinal cells derived from stem cells.
- Supporting Endogenous Repair: Transplanted stem cells might not only replace damaged cells but also secrete factors that stimulate the body’s own repair mechanisms.
How Stem Cells are Currently Being Used in Anti-Aging Therapies
Stem cells are already being put to work for anti-aging purposes. Here are four key areas in which stem cells are being utilized to help restore and rejuvenate.
- Skin Rejuvenation: The skin is our primary barrier against environmental aggressors and one of the most evident sites of aging. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been investigated for their potential to enhance collagen production, reduce inflammation, and promote angiogenesis, all essential for youthful skin.
- Facial Treatments: Some clinics offer stem cell facials, where stem cells (or more commonly, growth factors derived from stem cells) are applied topically to promote skin health, improve texture, and reduce signs of aging. The idea is that these growth factors can stimulate the skin’s own regenerative processes.
- Injectables: Similar to fillers, stem cells (especially adipose-derived stem cells) can be injected into specific areas of the face to promote collagen production, reduce wrinkles, and restore volume. They are sometimes combined with other treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for enhanced effects.
- Hair Regrowth: Hair loss, a hallmark of aging (especially in men) may benefit from stem cell therapies. By targeting the hair follicles with stem cell-derived treatments, there’s potential to reactivate dormant hair follicles and promote hair growth.
- Organ Regeneration: The prospect of generating entire organs from stem cells is exhilarating. While still in its infancy, there are ongoing attempts to create organs like the liver or heart using stem cell technologies, which could replace damaged organs without the need for transplants.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease might benefit from stem cell treatments. By replacing damaged neurons and supporting brain health, stem cells could potentially halt or reverse neurodegenerative processes. The goal is to replace damaged neurons and support overall brain health.
- Supplements and Topical Products: The market has seen a rise in stem cell-derived creams, serums, and even supplements. These products often contain growth factors and cytokines derived from stem cells and may promote skin health and slow the aging process.
Great Promise Lives Here!
Stem cells are making their mark in the anti-aging field, both in rigorous scientific research and commercial treatments. Their regenerative medicine properties offer a tantalizing promise, but as with all medical interventions, it’s crucial to approach them with a balance of optimism and caution. Here at AgeRejuvenation, our medical experts are leading the way in adapting stem cell technology. Is stem cell therapy right for you? The best way to find out is to schedule a free consultation with us today.