With Stem Cell and PRP patients will notice the following within 3-4 months.
Stage 1
Nourishes hair follicles from within*
Stage 2
Strengthens and promotes the growth of existing hair*
Stage 3
Promotes the growth of hair that has slowed or stopped growing*
Stage 4
Hair is noticeably stronger, healthier and more vibrant*
How Hair Grows – Stages
Hair grows from the follicle, or root, underneath the skin. The hair is ‘fed’ by blood vessels at the base of the follicle, which give it the nourishment it needs to grow. Between starting to grow and falling out years later, each hair passes through four stages: anagen, catagen, telogen and exogen. Every hair is at a different stage of the growth cycle.
Over time, the length of the anagen stage decreases. Therefore, the hair may become weaker and thinner after each cycle. That’s why it’s important to ensure your diet is rich in specific nutrients to maintain normal, healthy hair growth.
If you’re like millions of men and women, your once full, thick, shiny and (dare we say it) youthful looking hair has started to look dull, lifeless, dry and thinning as it ages. There are literally an infinite number of topical treatments and products on the market that claim to repair hair from the outside in. But you must understand hair growth phases and the hair growth cycle in order to understand how to maintain thicker, healthier looking hair from the inside.
Your head is made up of about 150,000 hair follicles. Around 80-90% of hair is in the anagen, or growing, phase of the hair growth cycle at any one time. Throughout the cycle, the hairs on your head are in various stages of growth and shedding. Below, find a step-by-step guide to the phases of the hair growth cycle.
Hair Growth Phases
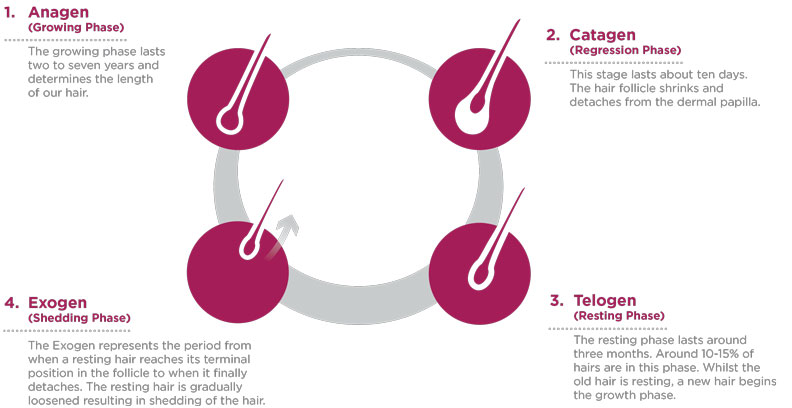
1. Anagen (Growing Phase)
The anagen, or growing, phase usually lasts 2-7 years, and the length of this phase determines the length of our hair.
2. Catagen (Transition Phase)
This is the transitional phase that lasts about ten days. During this stage, the hair follicle decreases in size and detaches from the dermal papilla.
3. Telogen (Resting Phase)
This is the telogen, or resting, phase, which generally lasts around 3 months. Around 10-15% of the hair on your head is in this phase at any given time. While the old hair is resting, a new hair begins the growing phase.
4. Exogen (Shedding Phase)
This is a part of the resting phase where the old hair detaches and sheds, and new hair continues to grow. Approximately 50 to 150 of your hairs may fall out daily. That is considered a normal rate of hair shedding.
Hair growth and hair shedding is impacted by a number of factors, including everyday stress, medication, age, heredity and damage caused by the environment, overstyling and poor nutrition.
As we age, the length of the anagen phase decreases, causing the hair to become weaker and thinner after each hair growth cycle. That’s why it’s important to ensure your diet is rich in specific nutrients to maintain normal, healthy hair growth.
When it comes to nutrition, a good diet and supplements with essential fatty acids, vitamins and minerals are important to help maintain healthy hair growth. Whatever we eat goes into our bloodstream, and our blood then delivers these nutrients via capillaries to the dermal papilla, which nourishes growing hair.
What happens to your body today is not going to affect your hair tomorrow. It takes a number of months, depending on the telogen phase of the hair growth cycle, to see the effects. So nourish your hair follicles with good nutrition, reduce your stress and avoid the use of damaging heat styling tools to reduce damage to hair strands. Take good care of tresses throughout the hair growth cycle to promote healthier, thicker looking hair.
If hairs enter the resting phase too early, excess shedding and noticeable thinning of the hair can occur.
Additional Resources
Hair Loss: The Science of Hair
How Hair Grows
Causes of Hair Loss
There are many factors that influence healthy hair growth. These encompass a wide range of emotional and lifestyle conditions that can prevent the body from effectively absorbing the essential nutrients it needs to support healthy hair.
Hair loss in Women
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes associated with menopause can affect the healthy hair growth cycle. While this menopausal side effect is relatively rare, it has been known to occur in some cases. Other hormonal changes in the body have been known to affect hair thinning and loss in some women. Women can experience problems with their hair due to a hormone imbalance and increased sensitivity to the male hormones found naturally in women’s bodies.
Post pregnancy
Pregnancy, while a beautiful and natural process, can be a stressful event for a woman’s body. Consequently, it’s common for women to experience hair thinning or even bald patches post-partum as their hormone levels normalize. However, this is usually a temporary condition and should reverse itself in time.
Birth control
The Pill is the most common form of contraception for women. It contains a mixture of progestin and estrogen, which occasionally can affect healthy hair growth in those who have a hereditary history of hair loss.
For men and women
Age
In our 20s and 30s, we typically have 615 hair follicles per square centimeter. The number falls to 485 by the time we turn 50, and to 435 by age 80. Each hair also becomes thinner, thereby reducing hair volume.
Stress
In the face of everyday stress, the adrenal gland produces more adrenaline, which can lead to an increase in the production of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). If you do not have enough other hormones to counterbalance this, it can lead to hair not being as healthy as it should be.
For some people, everyday stress can affect the condition of their hair and it can turn into a vicious circle: stress affects the hair cycle and the impact of this can cause more stress for the individual.
Poor diet
A diet rich in protein, vitamins and minerals is essential for healthy hair and hair growth. The hair follicle is a nonessential tissue and, therefore, one of the last tissues to receive nutritional substances. Therefore, any long-term deficiencies may lead to premature hair loss.
Protein
Eat at least five ounces (approximately 150 grams) of protein a day. Foods high in protein are meat, chicken, fish, beans, eggs, cheese and tofu. Because hair is made of 80% to 95% protein, this is an important area of your diet.
Iron
Iron deficiency can contribute to hair loss, especially in women and men who may lack adequate protein in their diets.
Other minerals
Other important minerals for healthy hair functioning are zinc (found in seafood and beans), silica (found in potatoes, red and green peppers, and bean sprouts), magnesium (found in green vegetables and nuts), and essential fatty acids (such as the omega fatty acids found in fish).
Overstyling
Excessive use of aerosol sprays, hair dyes, hair irons or curlers may result in damaged hair in the long term. Men and women who find their healthy hair is being affected may want to reconsider the products that they’re using on their hair and scalp, and consider other nutritional supplements and healthier styling methods.
Smoking
Smoking can affect healthy hair growth. Cigarette smoking has been shown to cause poor circulation, which can affect the amount of blood flow available to the hair follicles of the scalp.
Excessive Shedding
Thinning hair affects an estimated 21 million women in the U.S. Hair loss and excessive shedding can be caused by a wide range of factors, and the earlier the problem is addressed, the sooner you can find a solution. Here, find out everything you need to know about excessive shedding and hair loss.
Most women shed some hair every day. But occasionally, we find that we’re shedding more hair than normal. If you think you’re experiencing an unusually large amount of hair shedding or your hair has become dull and lifeless, consider what factors could be affecting the health of your hair.
Do You Have Hair Loss or Hair Shedding?
What is the difference between hair loss and hair shedding? How does hair loss differ from hair shedding, or are the two the same? As it turns out, there is a difference between hair loss and hair shedding. A minimal amount of hair shedding is actually quite common. Excessive shedding and hair loss are considered two distinct conditions. Excessive shedding is known as telogen effluvium, while hair loss is known as anagen effluvium. For more information about these two conditions, see this scientific study on nutritional factors and hair loss and the American Hair Loss Association’s information on effluviums.
What Is Normal Shedding?
You may be asking how many hairs is normal to shed per day. The body sheds around 100 hairs per day as a part of normal daily hair loss, with no visible effects on hair thickness. But if you regularly lose more hair than this in your hairbrush or the shower drain, you might be asking yourself, why is my hair shedding? If your hair is shedding more than usual, you could be suffering from excessive hair shedding. Hair shedding is typically a temporary condition associated with a particularly stressful life event, or it can be caused by hormonal changes, over-styling or nutritional deficiencies.
In contrast, hair loss, or anagen effluvium, happens when something stops hair from growing. Hair will not regrow until the cause of the condition is addressed. The most common causes of hair loss include hereditary hair loss, immune system overreaction, and certain drugs and treatments. Patients who undergo chemotherapy or other radiation treatments, for example, tend to lose a lot of hair. Their hair, however, usually regrows once the treatment has stopped.
In contrast, women who inherit the genes for hereditary hair loss may need medical treatment to regrow their hair. For women, hereditary hair loss typically manifests itself in the form of gradual thinning. Finally, tight hairstyles or braids that pull on the hair, or damaging products and hair color, can cause temporary hair loss.
Causes of Excessive Hair Shedding
What is extreme hair shedding and what causes hair shedding? It’s normal to shed around 100 or so hairs a day. These are the hairs you find in your shower, on your carpet and on the shoulder of your jacket. Most of the time, you won’t even realize that you are shedding these hairs.
If your body has increased hair shedding on a daily basis, however, you may have excessive hair shedding. There are many hair shedding causes, but a little-known fact is that curly hair is more likely to shed than thin hair. This is often because those with curly hair use more styling products and hot tools to manage their hair.
Known as telogen effluvium, excessive hair shedding is a temporary condition and typically affects those exposed to one or more physical or emotional stressors. Examples include people who are experiencing a difficult or traumatic life event, those who have lost 20 pounds or more, women who have recently given birth, women who have undergone an operation or are recovering from an illness, or women who have switched or stopped birth control pills. Often, the excessive shedding will not become apparent until a few months after the stressful event due to the hair growth cycle.
Does hair shedding stop on its own? Excessive shedding may stop when the body readjusts after the stressful event. Then, hair usually regains its previous fullness. People who are constantly under a lot of stress, however, may experience term excessive hair shedding.
Often, experts point to improper nutrition and lack of vitamins as a reason for hair shedding. Lack of proper nutrients, particularly insufficient protein, iron and essential fatty acids, can cause changes to the normal hair cycle, pushing roots prematurely up and causing them to fall out. The body requires a variety of nutrients in order to maintain hair health and growth.
Hair shedding caused by improper nutrition is easily remedied. Replenishing vital B vitamins and proteins likely will significantly improve hair health. Improper nutrition is one of the leading hair shedding causes. Those who cannot easily consume all necessary nutrients in their diets should consider taking clinically proven hair growth supplements that are specially formulated for women’s hair loss.
How to Stop Hair Shedding
If you’re now asking how to stop my hair from shedding, don’t panic! While constant hair shedding is worrisome, there are many different hair shedding treatments available. When choosing how to stop hair breakage and shedding, first you should is to stop actively damaging your hair. Heat damage from blow-dryers, curling irons and flat irons, as well as hair color, bleach and hair extensions are very common causes of female hair shedding.
Another way to reduce hair shedding is to identify and eliminate sources of physical or mental stress. Stop excessive hair shedding by getting rid of stress and putting yourself into a healthy physical and mental state. If you cannot stop the source of stress itself, try to change your reaction to it by adding de-stressing activities to your lifestyle, such as meditation, yoga, cardiovascular exercise or writing in a journal.
One of the best secrets to hair growth, thickness and shine lies within the body. If you provide your body with the nutrients it needs, it will grow thicker hair on its own. On the other hand, poor nutrition weakens hair and prematurely pushes out growing hairs, resulting in thinning, dull or shedding hair. Key nutrients for hair include proteins, Iron, Zinc, Vitamin C and B Vitamins. Take a daily hair multivitamin that contains all these nutrients in order to reduce hair shedding.

